A tooth infection might start as a small problem, but if left untreated, it can turn into something much more serious. Many people don’t realize how dangerous a tooth infection can be. So, can a tooth infection kill you? The answer is yes, it can, if the infection spreads and isn’t treated.
Ignoring symptoms like pain, swelling, or fever can lead to severe complications. In this article, we’ll explain what causes tooth infections, how they can spread, and why it’s so important to see a dentist right away if you suspect an infection.
| Key Takeaways If left untreated, a tooth infection can spread to vital areas, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like sepsis, brain infections, and even death. Symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, fever, and difficulty breathing or swallowing are key indicators that a tooth infection may be spreading and requires immediate attention. Professional treatment, such as antibiotics, root canal procedures, or even tooth extraction, is essential to stop the infection from progressing. Untreated tooth infections can lead to severe complications like Ludwig’s angina and meningitis, which can be fatal without urgent medical care. Maintaining good oral hygiene, scheduling regular dental check-ups, and addressing cavities early can help prevent tooth infections from occurring in the first place. |
What Causes a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection usually starts when bacteria enter the tooth through a cavity, crack, or injury. Once inside, the bacteria can spread to the tooth pulp (the soft tissue inside your tooth), leading to an infection.
Common causes of tooth infections include:
- Cavities: When plaque and bacteria build up on your teeth, they can cause decay, leading to a cavity that allows bacteria to enter the tooth.
- Gum disease: Infections in the gums can create spaces where bacteria can thrive and spread to the tooth.
- Trauma or injury: A cracked or chipped tooth provides an opening for bacteria to invade the tooth and cause an infection.
- Abscess formation: If the infection worsens, it can form an abscess, a pocket of pus that can spread the infection to other areas of the mouth or even the body.
Can a Tooth Infection Kill You?
Yes, a tooth infection can kill you if it is not treated in time. In the past, dental infections were one of the leading causes of death. For example, in London during the 1600s, they were listed as the fifth or sixth leading cause of death. Even in 1908, between 10 to 40 percent of dental infections resulted in death.
Today, while modern antibiotics and dental care have greatly reduced this risk, untreated infections can still cause severe complications. If the infection spreads to the bloodstream or other vital areas, it can lead to life-threatening conditions like sepsis or brain infections.
A tragic example of the severity of untreated tooth infections can be found in a story reported by ABC 10 News. According to the news outlet, a father from Northern California died after a tooth infection spread to his blood and lungs. The father, a truck driver, began experiencing a toothache while on the road. Despite seeking treatment and receiving antibiotics, the infection persisted and worsened. Eventually, the infection spread to his bloodstream and lungs, causing his death just four days later. This heartbreaking incident highlights how a seemingly minor dental issue can escalate into something fatal if not properly addressed.
Can a tooth abscess kill you? Yes, as this example shows, untreated abscesses and infections can have fatal consequences.
What Happens When a Tooth Infection Spreads?
Some of the most dangerous conditions that can result from a spreading infection include:
Sepsis
This is a severe, systemic infection that occurs when bacteria from the tooth infection enter the bloodstream. Sepsis causes widespread inflammation throughout the body, leading to organ failure, tissue damage, and in extreme cases, death. Symptoms of sepsis include high fever, rapid heart rate, confusion, difficulty breathing, and extreme weakness. Sepsis is a medical emergency and requires immediate attention to prevent life-threatening consequences.
Ludwig’s Angina
This is a rare but potentially deadly infection that spreads to the floor of the mouth, neck, and throat. The infection causes swelling, which can block the airways and make it difficult or even impossible to breathe. Ludwig’s Angina is usually caused by bacteria from a tooth infection spreading to the tissues beneath the tongue. If left untreated, it can quickly lead to respiratory distress and require urgent medical intervention to secure the airways and administer antibiotics.
Meningitis
In very rare cases, the bacteria from an untreated tooth infection can travel to the brain and cause meningitis. This is an infection of the protective membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord. Symptoms include severe headache, stiff neck, fever, confusion, and sensitivity to light. Meningitis can cause brain damage or death if not treated immediately, making it one of the most severe complications of a tooth infection.
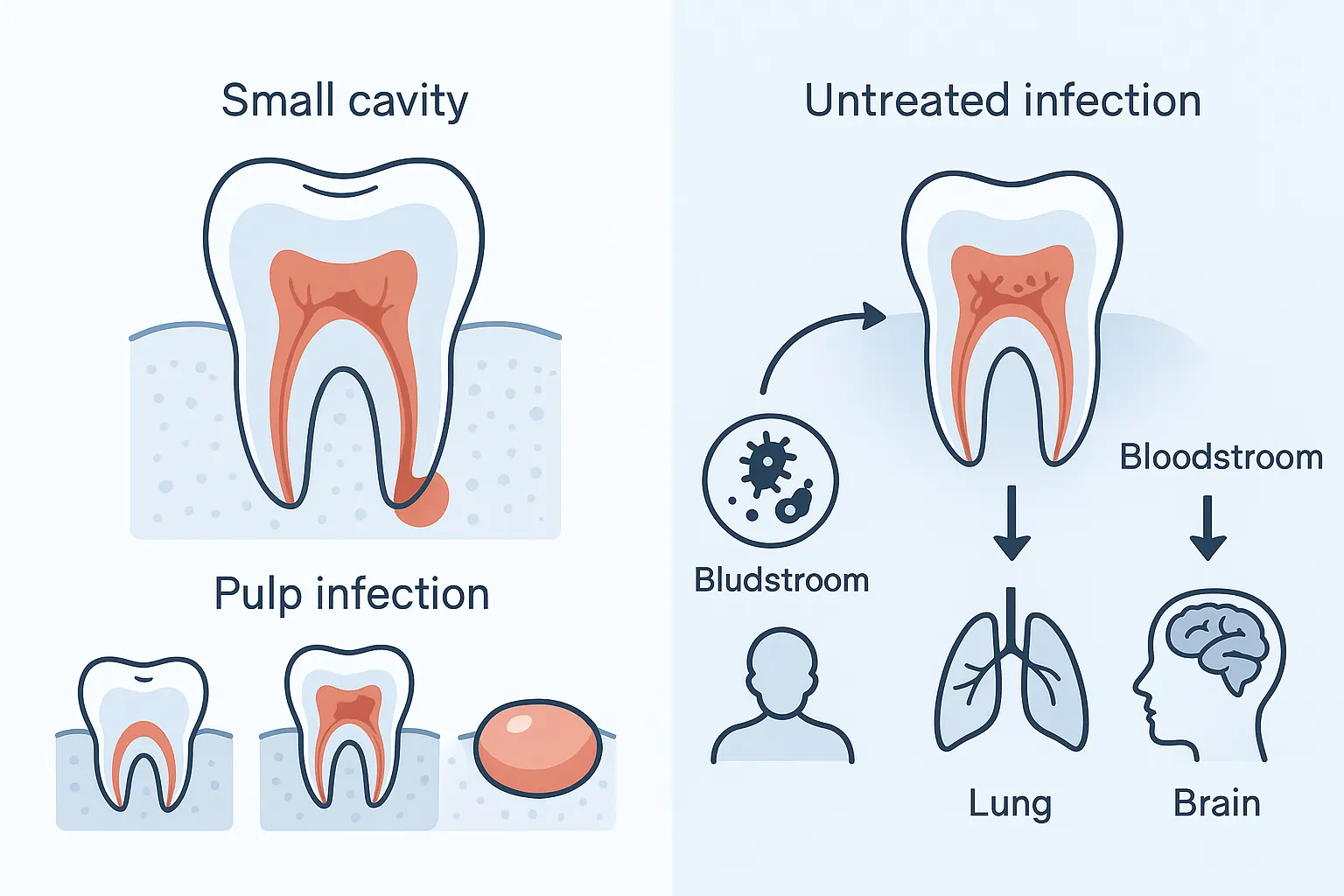
How Long Can a Tooth Infection Kill You?
How long can a tooth infection go untreated before it becomes fatal? A tooth infection can lead to death in a matter of weeks to months if left untreated. The timeline depends on how quickly the infection spreads and whether it reaches critical areas like the bloodstream or airways.
In general, once the infection enters the bloodstream, it can trigger sepsis, which can be fatal within hours if not treated. If the infection spreads to the neck or throat, it can block airways and lead to suffocation, often within a few days. Meningitis, a rare but serious complication, can develop within days and cause permanent brain damage or death if not treated urgently.
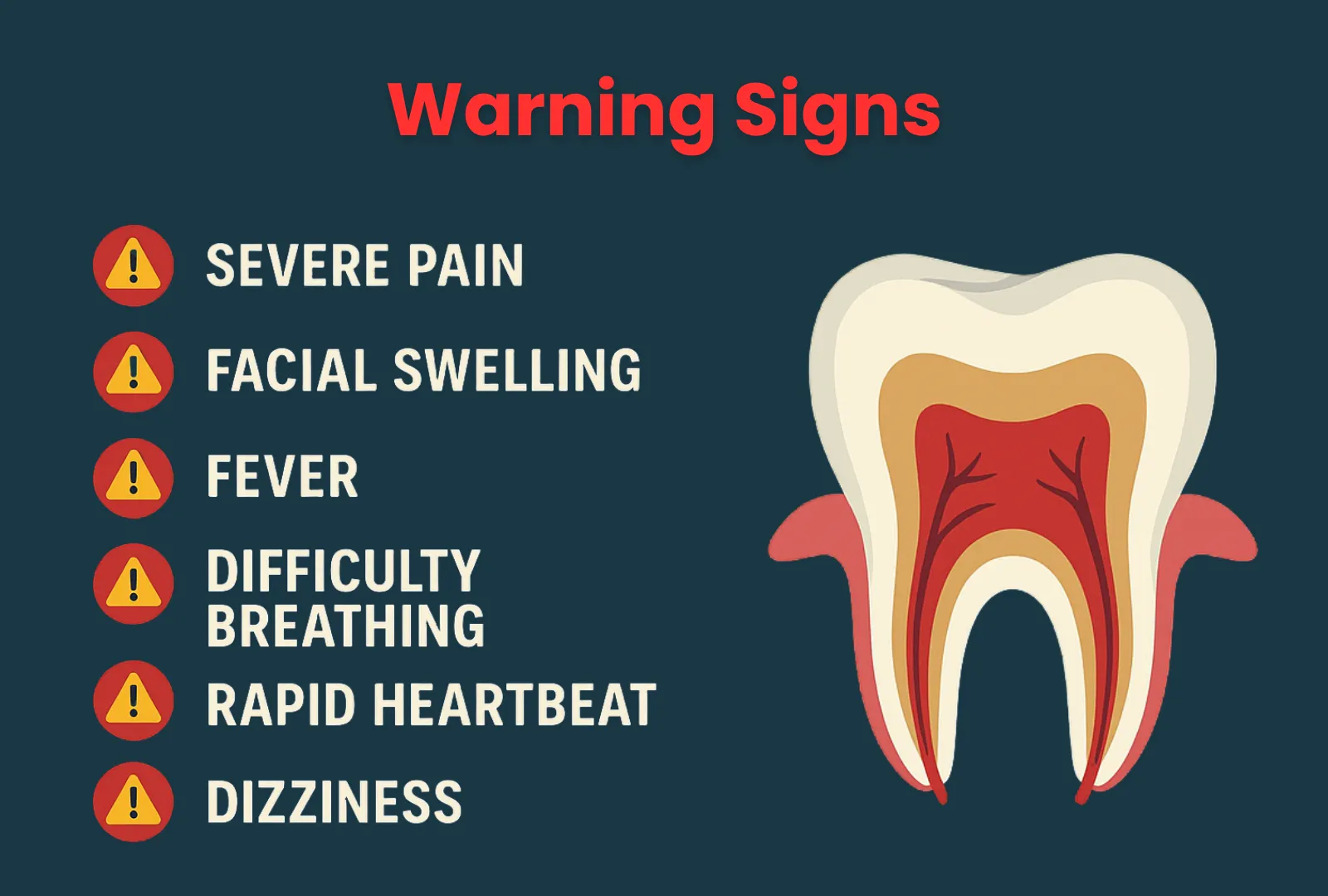
Signs That a Tooth Infection is Becoming Serious
If you have a tooth infection, it’s important to be aware of the warning signs that it may be worsening. When the infection becomes more severe, you may notice:
- Severe pain or throbbing: The pain may intensify, becoming more constant or sharp. It may spread to other areas of the face, jaw, or ear.
- Swelling: Noticeable swelling in the face, neck, or jaw can indicate that the infection is spreading. This can lead to difficulty swallowing or opening the mouth.
- Fever: A high fever is a sign that your body is fighting the infection. It can also indicate that the infection has spread beyond the tooth.
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing: This can happen if the infection spreads to the throat or neck, causing swelling that blocks the airways or the ability to swallow properly.
- Foul taste or odor: A bad taste in the mouth or a strong, unpleasant odor can mean there’s an abscess, indicating that pus is present and the infection is becoming more serious.
- Fatigue and general malaise: Feeling unusually tired, weak, or ill can signal that the infection is affecting your overall health.
Worried about a potential tooth infection? Schedule your consultation today!
When Should You Go to the Hospital for a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection won’t go away on its own, and it’s essential to get timely treatment to prevent it from spreading. If you notice symptoms like throbbing pain, swollen gums, or a persistent bad taste in your mouth, it’s time to see a dentist. However, if your infection has worsened and you develop additional serious symptoms, you should go to the hospital or an urgent care center immediately.
Seek emergency care if you experience:
- Fever
- A general feeling of unwellness (malaise)
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Swelling around your face, neck, or eyes
- Inability to open your mouth or jaw
- Trouble speaking, chewing, or swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- Rapid heart rate
If something doesn’t feel right, trust your instincts and seek medical help. Even if your symptoms aren’t caused by a tooth infection, they could be due to another serious health condition that needs immediate attention.
Can a Tooth Infection Be Treated at Home?
While waiting for professional treatment, there are some home remedies that may help ease the pain and discomfort caused by a tooth infection. However, these should only be used as temporary measures and should never replace seeing a dentist.
Here are some common home remedies you can try:
- Over-the-counter pain medications like ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), naproxen (Aleve), or acetaminophen (Tylenol) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Eating soft foods and chewing on the opposite side of your mouth from the infected tooth to avoid further irritation.
- Avoiding foods and drinks that may irritate the infected tooth, such as those that are very hot or cold, acidic, spicy, or hard/crunchy.
- Using a soft-bristled toothbrush to clean your teeth, and be careful to avoid flossing around the affected tooth to prevent further irritation.
- Rinsing your mouth with a saltwater or hydrogen peroxide rinse to help alleviate pain and swelling.
- Applying a cold compress near the affected area to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Using garlic, which has natural antimicrobial properties, to apply gently to the infected tooth.
Treatment Options for Tooth Infections
To treat a tooth infection effectively, professional dental care is essential. Depending on the severity of the infection, the following treatment options may be recommended:
- Antibiotics: If the infection has spread, antibiotics are usually prescribed to kill the bacteria and prevent further spread. In some cases, if the infection is severe, antibiotics may be given intravenously in a hospital setting.
- Root Canal Treatment: For infections that affect the pulp of the tooth, a root canal may be necessary. This procedure removes the infected tissue inside the tooth and seals it to prevent further infection.
- Tooth Extraction: In cases where the infection is severe and the tooth cannot be saved, a dentist may recommend extraction. This helps remove the source of the infection and prevent it from spreading further.
- Abscess Drainage: If an abscess (a pocket of pus) has formed, the dentist may need to drain it to relieve pressure and remove infected material. This can be done through a small incision in the gum.
How Do You Know if a Tooth Infection is Killing You?
In rare and extreme cases, a tooth infection can become fatal if you experience severe symptoms such as:
- Intense pain that doesn’t respond to medication
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- High fever, confusion, and rapid heartbeat
- Swelling that makes it hard to open your mouth or breathe
- Symptoms of sepsis, including dizziness, chills, and a drop in blood pressure
Prevention: How to Avoid Tooth Infections
Preventing tooth infections begins with good oral hygiene and regular dental visits. Simple habits can make a big difference in keeping your teeth and gums healthy:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss daily to remove plaque between your teeth.
- Limit sugary foods and drinks that can cause cavities.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
- Treat cavities and gum disease early to avoid infection.
Worried about a potential tooth infection? Schedule your consultation today!
Frequently Asked Questions
How long can you live with an untreated tooth infection?
An untreated tooth infection can quickly become dangerous, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions like sepsis or Ludwig’s angina. If left untreated, the infection can spread in as little as a few days. The sooner you address the infection, the better your chances are of avoiding severe complications.
What are the signs that a tooth infection has spread to the rest of your body?
When a tooth infection spreads, you may experience symptoms like high fever, swelling in the face or neck, difficulty breathing, or swelling of the lymph nodes. If you notice these symptoms, it’s critical to seek emergency care immediately.
How long does it take for a tooth nerve to die after an infection?
If the infection reaches the tooth’s nerve, the nerve can die within a few days to weeks if untreated. The pain may initially subside as the nerve dies, but the infection will continue to spread, causing further damage.
How quickly can a tooth infection spread?
A tooth infection can spread within days to weeks if left untreated. In severe cases, it can escalate more rapidly, leading to systemic infections that affect vital organs like the heart, brain, and stomach.
